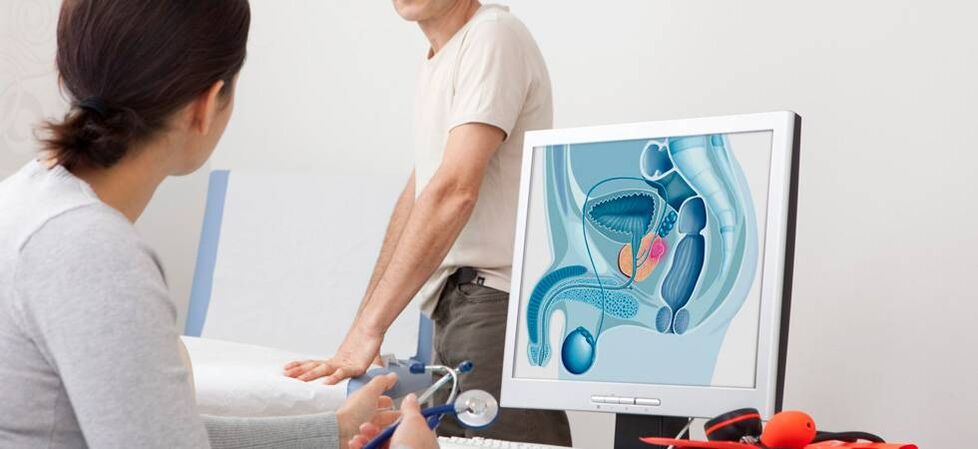
The pathology of the prostate gland, which develops due to inflammatory processes in it, is called the disease - prostatitis.
The development of pathology
More often than others, an infectious form of prostatitis occurs. The infection capable of impressing the prostate by penetrating from the urethral hole or other organs and glands of the genitourinary system.
The high probability of infection of the organ is due to the adjacent localization of the anus and urethral canal.
With this likelihood, statistics detect an inflammatory inflammation of the prostate in men, which is associated with the fitness of the organ to infected neighbors.
Even the presence of infection in the prostate does not ensure the development of inflammation.
Inflammation of the prostate occurs with the joint action of pathogenic microorganisms and provoking factors.
The causes of prostatitis
Every man, taken by surprise or understanding the inevitability of the disease due to the exacerbation of provoking factors, can guess about the course of prostatitis.

The prostate gland is a place for the transit of the urethral canal, therefore, the inflammatory process in a sick organ, leading to an increase in its structures, leads to a violation of the emptying of the bladder.
When establishing a diagnosis for different forms of inflammation of the prostate gland, binary nomenclature is used:
- Chronic non -infectious
- Chronic infectious
- Acute infectious
- Acute non -infectious
Varieties of prostatitis are due to a complex of provoking factors under certain circumstances.
The first factor that is statistically prevailing in men of young and pre -retirement age - infections transmitted from the sexual partner.
Venus diseases, especially in the stage of symptomatic remission, are able to leave behind an infection in a hidden state or prostate lesions, which progressive even after the elimination of an infectious agent.
Infection can supplement the infection, systematic overeating, nutrition of acute, excessively oily, calorie carbohydrate foods.
This is how non -infectious prostatitis occurs and the course of a non -infectious variety is enhanced.
Provocing factors are hypothermia and age -related changes in the prostate.
Signs of prostatitis in men
It is difficult to diagnose an infectious or non -infectious form of inflammation of the prostate, based only on the similarity of symptoms.
If the following signs of prostatitis are detected, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of methods for detecting the disease:
- During the emptying of the bladder, pain and intensity are experienced, after the end of urination, the patient feels a burning sensation in the urethra;
- body temperature exceeding normal;
- The feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder after the end of the urination does not leave the sick man for some time;
- Pain in the period between urination is felt in the perineum, inguinal and abdominal zones, reflected in the legs, buttocks, pelvis and sacrum;
- lethargy and malaise.
A man can form suspicion of prostatitis if at least two of them become noticeable from the entire list and symptoms.
A specific sign of the inflammatory process in the prostate is the temperature difference measured in different parts of the body.
The pattern of temperature changes is associated with the localization of the focus of inflammation: the closer to it, the higher the temperature.
When measuring the temperature in the oral cavity, deviations from the norm are not observed, in the armpits - a subfebrile temperature, in the rectum the parameter value exceeds the norm larger than by a degree.
The pain symptom develops with an increase in intensity as inflammation increases in the prostate.
The typical occurrence of pain is characteristic of the process of emptying the bladder, during the day the pain extends to the rectum and the entire area of the perineum.
The intensity of pain increases with a small to unbearable.
Purder and malaise can be accompanied by dizziness and headaches, small nausea attacks, drowsiness.
If such symptoms are detected, a urine delay is suspected, as a result of which the general intoxication of the body develops protein decay products.

Deviations in urination are associated with the sluggishness of the jet, a long drip release of urine, not imminent formation of a jet and calls to emptying the bladder in the absence of urine release.
Possible complications
Complications after prostatitis occur in the absence of medical intervention in the course of the disease or improper compiling a treatment regimen.
Medical practice shows the most frequent distribution after prostatitis:
- lack of erection and ejaculation;
- the spread of the inflammatory process to the nearby organs of the genitourinary system;
- cytological disorders leading to the inability of sperm to fertilize the eggs;
- decrease in libido;
- Psychoneurotic states that reduce the quality of life and the state of health of a man as a whole.
After prostatitis, the penis sharply reduces the ability to harden and be filled with blood. Possible sexual contacts end quickly compared to the recent full -fledged sex life. Not all sexual contact ends with ejaculation.
If such deviations are detected, a comprehensive diagnostic test is required.
With the spread of the inflammatory process to the urethra and bladder, cystitis and urethritis develop.
With the development of the latter, pain of a sharp nature appears, the process of impaired urine outflow (its delay or incontinence) threatens to switch to a chronic level. The performance of a man in this state is doubtful.
Erectile dysfunction leaves behind a number of psychological and therapeutic problems that need competent medical correction.
The impossibility of cavernous bodies to be filled with blood is explained by the edematous state of the prostate and the associated genitourinary organs.
The blood supply to the penis, necessary for an erect state, becomes problematic.
Psychologically, the third part of men who has been developed by consequences after prostatitis suffers in severe form.
The state of a man can normalize only during long -term psychological work with the patient against the background of drug therapy. Failures in sexual life impede the further desire to continue sexual life.
Prostatitis can provoke a violation of the acid-base composition of sperm, reflected on the fertilizing capacity of sperm.
The result of the pathology is infertility in a man of the first degree. It is important in this state to timely eliminate the cause of infertility due to the lack of the opportunity to cure infertility of the second degree with a drug method. Proper treatment can be prescribed by andrologist or urologist. That is why men should not ignore the signs of prostatitis.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic examination scheme is directly dependent on those complaints and signs with which the patient addresses the urologist or andrologist.
Diagnosis of prostatitis in men can be performed both at home and in a medical institution.
The initial diagnostic stage is data collection for an anamnesis. The doctor performs an external inspection of the genitals and listens to the patient's complaints.
Based on the initial data, a scheme of further diagnostic study of a sick man is set.
During the collection of an anamnesis, the doctor finds out the duration of the symptoms that appeared, the presence of previously shown prostatitis, a list of diseases by the patient, risk factors for the development of the disease, a possible list of transmitted sexually transmitted diseases, the development of signs of the disease, the presence of sexual partners and sexual relations.
At the present stage of the development of medicine, the list of questions is posted in the questionnaire, which the patient fills out before the visit to the doctor’s office. Thus, the time of the patient and the doctor is saved.
The first mandatory stage of examination of the patient with signs on prostatitis is the study of the prostate gland from the rectum.
The doctor determines the degree of increase in the inflamed organ, its density, the uniformity of the consistency or the presence of nodes, or seals, the degree of pain during palpation.
Before the palpation, the intestinal cavity is performed.
In the absence of an inflammatory process in the prostate, there are no pain, with prostatitis, the intensity of pain can be different, and their localization is felt in the groin, rectum, perineum, and sacrum. In this case, it is contraindicated in a number of procedures, for example, cystography.
For a microscopic examination of the secretion of the prostate gland, the patient is performed by massage of the prostate through the rectum.
With the desire to urinate until the end of the prostate massage, this cannot be done until a drop of the prostate secretion from the urethral opening is taken for analysis.
The procedure ends in conducting the subject glass of the microscope along the hole of the urethra, after which the smear is painted and microscopic analysis according to the following parameters:
- the presence of leukocytes and the calculation of their quantity;
- lecitin quantity;
- The activity of pathogenic microorganisms and their presence.
The detection of bacteria in the field of view of the smear indicates the infectious type of prostatitis.
The number of leukocytes in the field of view of more than 2 indicates the inflammatory process in the prostate.
For a reliable result of a microscopic examination, it is necessary to correctly take a fence for analysis and competently paint the drug.
The above tests are mandatory, additional examinations are prescribed by the doctor selectively, depending on the doctor’s suspicions on the nature of inflammation.
The analysis of the secret of the urethra is carried out by a tool similar to a catheter. On top of the metal coating, cotton wool is wound.
Before passing the analysis, urination is excluded for 2-3 hours. Otherwise, microflora is washed into the external environment.
The doctor introduces a cotton swab of approximately 4 cm inside the hole of the penis and makes rotational movements. A smear from the urethra is investigated for the presence of DNA and bacteria residues.
Analysis of urine is a means of detecting blood cells: red blood cells and leukocytes, protein (normally absent or present in trace amounts).
When making errors in the analysis of the urethra smear and prostatitis symptoms, urine sowing for bacteriological analysis is prescribed.
The disadvantage of the method is the long -term expectation of a colony of pathogenic microorganisms (up to 1 week).
Sowing is carried out by a comparative method after the fence of three portions of urine (beginning, middle and end of the emptying of the bladder).
A larger number of pathogenic microorganisms in one of the samples gives the basis for the assumption of the localizing focus of infection.
The detection in the first part of the urine of bacteria does not give a reason to confirm inflammation.
The second and third part of the urine, in excess of the number of detected microorganisms, give the basis for clarifying the localization of inflammation (in the urethra and the bladder - respectively).
The degree of deviation of the sexual function from the norm is checked by the analysis of sperm for viscosity and other physico-chemical indicators of the environment, the activity and viability of male gametes, and a spermogram is rarely prescribed.
The urofloometric method is not often arranged. If the possibility and addition of the picture of the changes taking place, a urodynamic examination of the urinary tract is carried out.
An ultrasound examination specifies the density of the sick organ and other parameters obtained after a finger examination of the prostate through the rectum.
The prostate gland is visible in two ways: transrectal ultrasound and ultrasound through the abdominal cavity.
In case of suspicion of adenoma and prostate cancer, the doctor can prescribe an additional cytoscopic examination of blood, the so -called dog test.
The fence is made from a vein, a blood test establishes (excludes) the presence of RSA protein, which appears with malignant tumors.
At home, the patient can suspect prostatitis, focusing on the color and turbidity of urine, symptoms of the disease.
How to treat at home
Supply of pharmaceuticals
If signs of prostatitis appear, men should not self -medicate, drugs should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Preparations proposed for healing prostatitis are distinguished by a variety of forms and pharmaceutical properties. More often than others are prescribed candles for rectal use.
The rationale for the choice of doctors is associated with the proximity of the effects of the components of rectal suppositories and the prostate gland.
The condition for the effective effect of the active substance of candles on the organ tissue is the patient’s peace in a lying position for 30 minutes after the administration of the rectal drug. Candles inactivate pathogenic microflora and have an analgesic effect.
Intramuscular and intravenous injections contribute to the most rapid effect on the sick organ through spread through the bloodstream.
Immediately after urination, instillations are prescribed aimed at penetrating medicinal substances into the prostate through the urethral hole. The maximum amount of administration is 5 ml.
Table forms for prostatitis are better known as antibiotics divided into 3 groups and successfully cope with the possible spectrum variety of types of pathogenic microflora:
- Tetracyclines
- Fluoroquinolones
- Penicillins
Warm microclisms with introduced substances are carried out in the evening.
The main condition for using the enema is the inadmissibility of the gland strain and compliance with the temperature regime. Refers to folk methods of treating prostatitis.